A Few Things You (Probably) Don’t Know About Thanksgiving
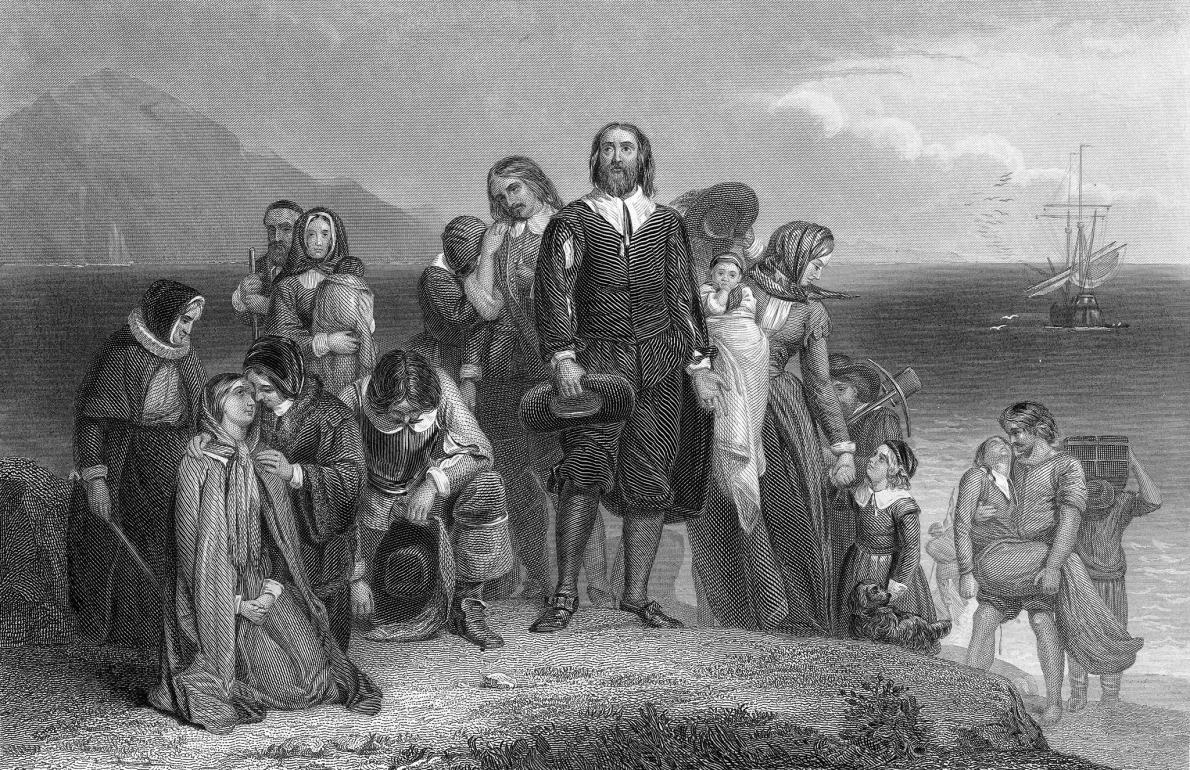
The pilgrims stole from graves, the Wampanoag were devastated by disease, and the peace between them was political.
When the Mayflower pilgrims and the Wampanoag sat down for the first Thanksgiving in 1621, it wasn’t actually that big of a deal. Likely, it was just a routine English harvest celebration. More significant—and less remembered—was the peace treaty that the parities established seven months earlier, which lasted for 50 years.
“There’s in fact very little historical record of the first Thanksgiving, which is why Thanksgiving wasn’t really celebrated as a holiday until the 19th century,” says Charles C. Mann, author of 1491: New Revelations of the Americas Before Columbus. “To historians, it seems kind of funny that the celebration … now seems more important than the treaty itself.”
President Abraham Lincoln established Thanksgiving as a national holiday during the Civil War, and the feast has since become an American tradition. Yet the story of the Wampanoag and the pilgrims who first broke bread is not commonly known. (Learn about National Geographic Channel’s new drama about their story.)
Here’s a little background about the much-mythologized meal.
1. It wasn’t actually a “Thanksgiving.”
In 1841, Boston publisher Alexander Young printed a book containing a letter by pilgrim Edward Winslow, which described the feast:
“[O]ur harvest being gotten in, our governor sent four men on fowling, that so we might after a more special manner rejoice together … [There were] many of the Indians coming amongst us, and among the rest their greatest King Massasoit, with some ninety men, whom for three days we entertained and feasted.”

Among 17th-century pilgrims, a “Thanksgiving” was actually a period of prayerful fasting, and Winslow did not use the word anywhere in his letter. But when Young published the letter, he called it the “first Thanksgiving” in a footnote, and the name stuck. (Read what the Wampanoag and pilgrims ate at their feast.)
2. A year before the first Thanksgiving, the pilgrims raided Native American graves.
When the pilgrims arrived in Cape Cod, they were incredibly unprepared. “They were under the persistent belief that because New England is south of the Netherlands and southern England, it would therefore be warmer,” says Mann. “Then they showed up six weeks before winter with practically no food.”
In a desperate state, the pilgrims robbed corn from Native Americans graves and storehouses soon after they arrived; but because of their overall lack of preparation, half of them still died within their first year. To learn how to farm sustainably, they eventually required help from Tisquantum, an English-speaking Native American who had been staying with the Wampanoag.
3. The pilgrims could only settle at Plymouth because thousands of Native Americans, including many Wampanoag, had been killed by disease.
If the pilgrims had arrived in Cape Cod three years earlier, they might not have found those abandoned graves and storehouses … in fact, they might not have had space to land.
Europeans who sailed to New England in the early to mid-1610s found flourishing communities along the coast, and little room for themselves to settle. But by 1620, when the Mayflower arrived, the area looked abandoned.
“A couple of years before, there’d been an epidemic that wiped out most of the coastal population of New England, and Plymouth was on top of a village that had been deserted by disease,” says Mann.
“The pilgrims didn’t know it, but they were moving into a cemetery,” he adds.
4. The peace that led to the first Thanksgiving was driven by trade and tribal rivalries.
Before the Wampanoag suffered losses from disease, they had driven Europeans like John Smith away. “Now,” says Mann, “the Wampanoag [were] much weaker because of the disease, and they’re much weaker than their hated adversaries, the Narragansett.”
Ann McMullen, curator at the National Museum of the American Indian, says that the Wampanoag weren’t necessarily looking to make alliances against the Narragansett; but “because the Wampanoag were in a slightly weakened position,” they realized that an alliance with the pilgrims “could fortify their strength.”
The Europeans were valuable trading partners for the Wampanoag and other Native Americans in the area because they traded steel knives and axes for beaver pelts—something that, in the beaver-rich New England area, the Wampanoag considered essentially worthless.
“It’s a little like somebody comes to your door, and says I’ll give you gold if you give me a rock,” Mann says. “The Wampanoag thought: if we tie ourselves to these guys, everybody else will be hesitant to attack us, because they could drive away these people who are willing to pay gold for rocks.”
Политика конфиденциальности | Правила пользования сайтом